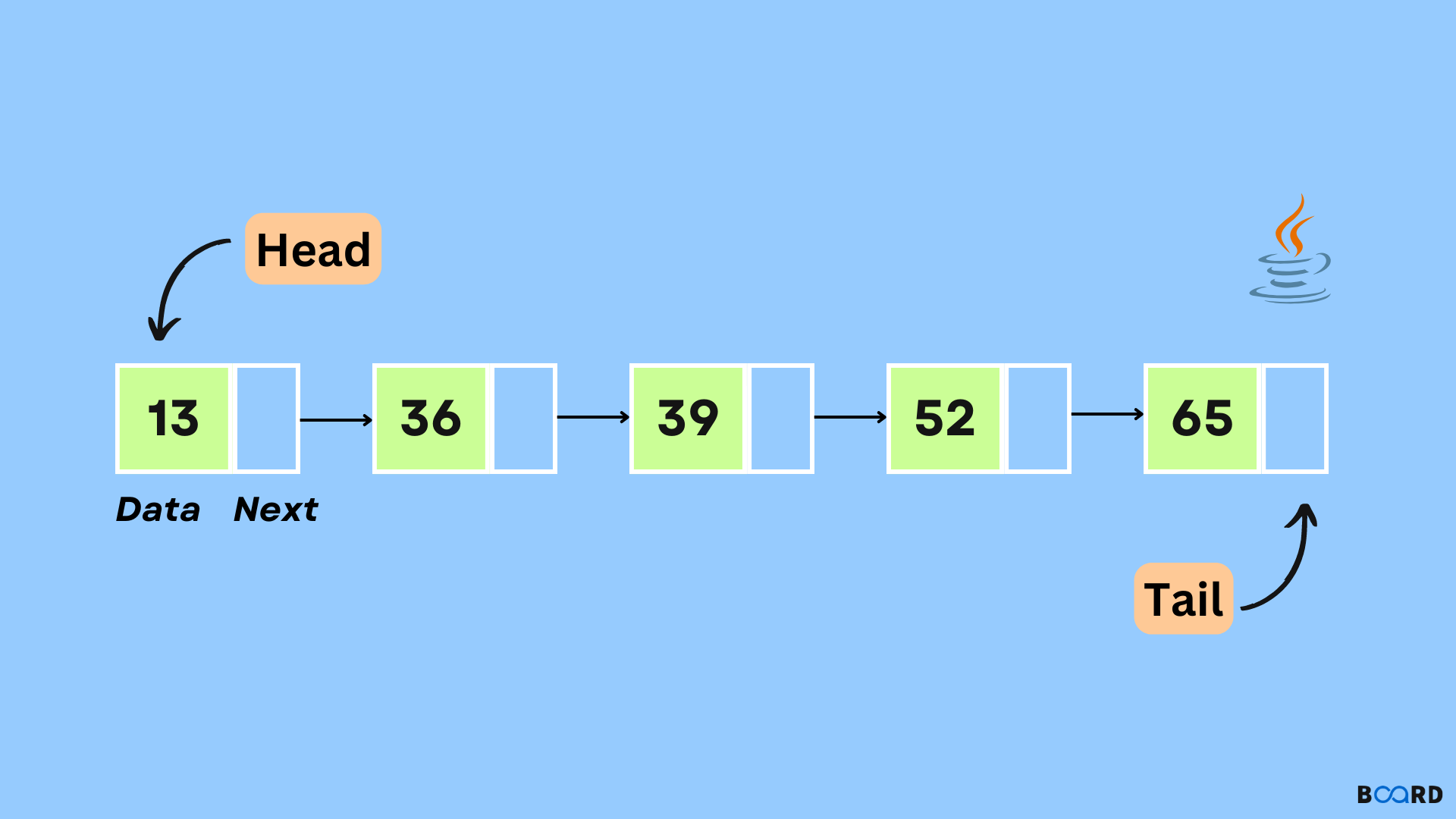
A Linked List is, as the word implies, a list where the nodes are linked together. Each node contains data and a pointer. The way they are linked together is that each node points to where in the memory the next node is placed.
Linked Lists
A linked list consists of nodes with some sort of data, and a pointer, or link, to the next node.
A big benefit with using linked lists is that nodes are stored wherever there is free space in memory, the nodes do not have to be stored contiguously right after each other like elements are stored in arrays. Another nice thing with linked lists is that when adding or removing nodes, the rest of the nodes in the list do not have to be shifted.
Linked Lists vs Arrays
The easiest way to understand linked lists is perhaps by comparing linked lists with arrays.
Linked lists consist of nodes, and is a linear data structure we make ourselves, unlike arrays which is an existing data structure in the programming language that we can use.
Nodes in a linked list store links to other nodes, but array elements do not need to store links to other elements.
Singly Linked List
It is the simplest type of linked list in which every node contains some data and a pointer to the next node of the same data type.
Doubly Linked List
A doubly linked list or a two-way linked list is a more complex type of linked list that contains a pointer to the next as well as the previous node in sequence.
Circular Linked List
A circular linked list is that in which the last node contains the pointer to the first node of the list.