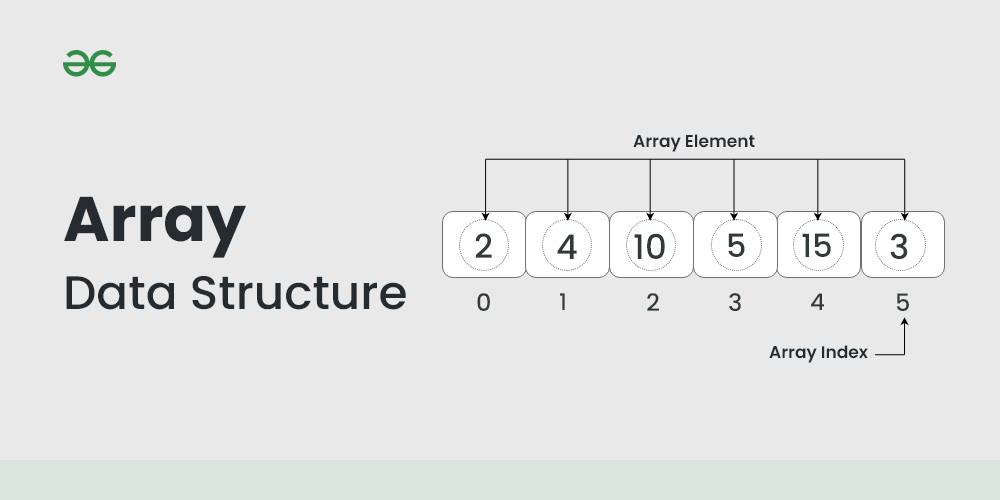
An array data structure is a fundamental concept in computer science that stores a collection of elements in a contiguous block of memory. It allows for efficient access to elements using indices and is widely used in programming for organizing and manipulating data.
Why Do You Need an Array in Data Structures?
Let’s suppose a class consists of ten students, and the class has to publish their results. If you had declared all ten variables individually, it would be challenging to manipulate and maintain the data.
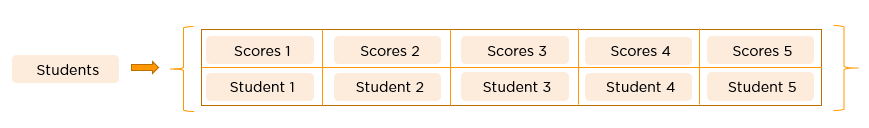
There are two main types of arrays:
- One-dimensional arrays: These arrays store a single row of elements.
- Multidimensional arrays: These arrays store multiple rows of elements.
Properties of array
There are some of the properties of an array that are listed as follows –
- Each element in an array is of the same data type and carries the same size that is 4 bytes.
- Elements in the array are stored at contiguous memory locations from which the first element is stored at the smallest memory location.
- Elements of the array can be randomly accessed since we can calculate the address of each element of the array with the given base address and the size of the data element.